M/35 24039871
c.c leg tingling sensation
응급실 기록
#HBP
환자 금일 10시 50분부터 갑지가 양측 대퇴부 근육 힘이 안들어가며 넘어졌다고 하며,
이후로 증상 지속되어 내원함.
내원 당시는 초반보다 호전되어 motor 3 정도
Td (-) pain (-) SLR (-)
trauma (-)
back Td (-) pain (-)
응급실 검사
LAB >
Sodium 140
Potassium 2.5 ▼
Chloride 106
cardiac marker > WNL
xray > WNL
Adm 기록 (ME / MN)
R/O Primary aldosteronism
상환 both leg weakness, tingling sensation 주소로 응급실 내원하였고,
initial lab 상 Potassium 2.5, HTN 확인되어 r/o Primary aldosteronism 하에 본과 연결됨.
환자 기술직 근무자로 몸을 많이 쓰는 일을 한다고 하며,
올해 1월 오른쪽 두번째 발가락 골절되어 근무를 쉬다가 올해
3월 local OS 병원에서 골절부위 유합됐다는 이야기를 듣고 다시 근무 시작하였다고 함.
그때부터 무거운 것을 들거나 옮길 때 간헐적으로 양쪽 허벅지의 tingling sensation 이 있어 local OS 진료를 봤고,
근이완제 처방받아 증상이 있을 때 마다 prn 으로 복용하였음.
금일 22:50 경, 영화관에서 영화를 보고 일어서는 데 양쪽 허벅지에 힘이 거의 들어가지 않았다고 하며 부축을 받아 겨우 일어나기는 했으나 한 두 걸음 걸은 뒤 양쪽 허벅지 힘이 완전 풀려 그대로 바닥에 주저 앉았다고 함.
ER 내원 당시에는 motor Gr. 3 정도로 회복되었으며, 양쪽 다리를 lateral rotation 하여야 겨우 위로 들 수 있는 수준임. sensory intact.
스스로 앉을 수는 있지만 일어설 수는 없는 수준.
약 10년 전(25세), 혈압을 잴 때마다 높게 나와 병원진료를 본 적이 있으며
1개월 동안 local 내과의원에서 고혈압약을 처방받아 복용한 뒤 혈압 정상화 되어 중단하였다고 함.
최근 음주한 적 없으며, 설사/구토 등의 event 없었음.
PLAN>
1) Admission
2) Primary aldosteronism work up
3) Potassium 교정, Spironolactone 으로 혈압 조절 고려
4) Spot UA, 24hr UC 확인, TTKG 계산
5) Lypmphodominant CBC 에 대한 evaluation
경과기록 7/5
Free T4 4.58 ▲
T3 (Triiodothyronine) CLIA 4.120 ▲
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) CLIA 0.01 ▼
R/O Grave's disease (갑상선 항진증)
PLAN >
내일 thyroid scan, uptake 검사
thyroid antibody
e' f/u
case review > hypokalemia

ECG >

Hypokalemia results in
- slowed conduction,
- delayed ventricular repolarization,
- shortened refractory period and
- increased automaticity.
ECG changes include
- flattening and inversion of T waves in mild hypokalemia,
- followed by Q-T interval prolongation,
- visible U wave and mild ST depression in more severe hypokalemia.
- Severe hypokalemia can also result in arrhythmias such as Torsades de points and ventricular tachycardia.
Sx >
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Muscle cramps or twitching
- Constipation
- Arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythms)
cause > vomit, diarrhea, kidney problem, medication(diuretics)
- Cushing's syndrome
- Gitelman syndrome
- Liddle syndrome
- Bartter syndrome
- Fanconi syndrome





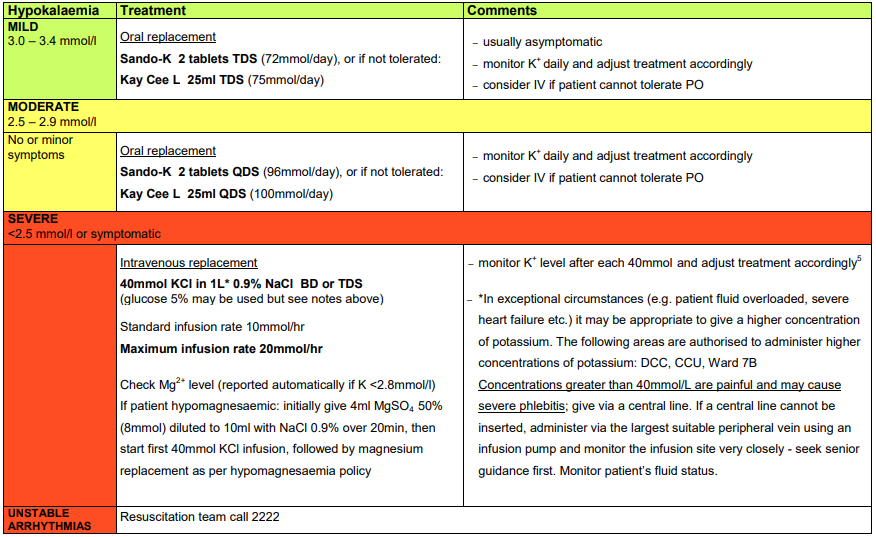
case review >



Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis
Hypokalemic thyrotoxic periodic paralysis TPP
is a potentially life-threatening complication of hyperthyroidism,
defined by 3 characteristic features:
- thyrotoxicosis
- hypokalemia
- acute painless muscle weakness
severe muscle weakness.+ high levels of thyroid hormone in their blood (hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis).
Causes
This is a rare condition that occurs only in people with high thyroid hormone levels (thyrotoxicosis). Men of Asian or Hispanic descent are affected more often.
There is a similar disorder, called hypokalemic, or familial, periodic paralysis. It is an inherited condition and not related to high thyroid levels, but has the same symptoms.
Risk factors include a family history of periodic paralysis and hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms
Symptoms involve attacks of muscle weakness or paralysis. The attacks alternate with periods of normal muscle function. Attacks often begin after symptoms of hyperthyroidism have developed. Hyperthyroid symptoms may be subtle.
The weakness or paralysis:
- Comes and goes
- Can last from a few hours up to several days (rare)
- Is more common in the legs than the arms
- Is most common in the shoulders and hips
- Is triggered by heavy, high-carbohydrate, high-salt meals
- Is triggered during rest after exercise
Other rare symptoms may include any of the following:
- Difficulty breathing
- Speech difficulty
- Swallowing difficulty
- Vision changes
People are alert during attacks and can answer questions. Normal strength returns between attacks. Muscle weakness may develop over time with repeated attacks.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Excessive sweating
- Fast heart rate
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Heat intolerance
- Increased appetite
- Insomnia
- More frequent bowel movements
- Sensation of feeling a strong heartbeat (palpitations)
- Tremors of the hand
- Warm, moist skin
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
The health care provider may suspect thyrotoxic periodic paralysis based on:
- Abnormal thyroid hormone levels
- A family history of the disorder
- Low potassium level during attacks
- Symptoms that come and go in episodes
Diagnosis involves ruling out disorders associated with low potassium.
The following signs may be seen during the attack:
- Decreased or no reflexes
- Heart arrhythmias
- Low potassium in the bloodstream (potassium levels are normal between attacks)
Treatment
Potassium should also be given during the attack, most often by mouth. If weakness is severe, you may need to get potassium through a vein (IV). Note: You should only get IV if your kidney function is normal and you are monitored in the hospital.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If an attack isn't treated and the breathing muscles are affected, death can occur.
Chronic attacks over time can lead to muscle weakness. This weakness can continue even between attacks if the thyrotoxicosis is not treated.
Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis responds well to treatment. Treating hyperthyroidism will prevent attacks. It may even reverse muscle weakness.